What is visibility?
Visibility refers to the maximum distance at which a person with normal vision can identify a target from the background. This is actually a very subjective indicator, and different people may get different visibility. Therefore, the value of visibility is never absolute. Weather visibility depends on the current meteorological environment.
Fog, haze, dust and even rain and snow can cause visibility to decrease. Usually we measure visibility in two ways: manual measurement and equipment measurement. Manually observed visibility generally refers to effective horizontal visibility. It is the maximum horizontal distance of a target that can be seen in more than half of the field of vision. At present, most weather stations use equipment to measure, but in weather such as dust and sand, manual measurement is more accurate. The visibility measured by the equipment is expressed in meteorological optical range. Meteorological optical range refers to the path length through which the luminous flux of a parallel beam of light with a color temperature of 2700K emitted by an incandescent lamp is weakened to 5% of the initial value in the atmosphere.
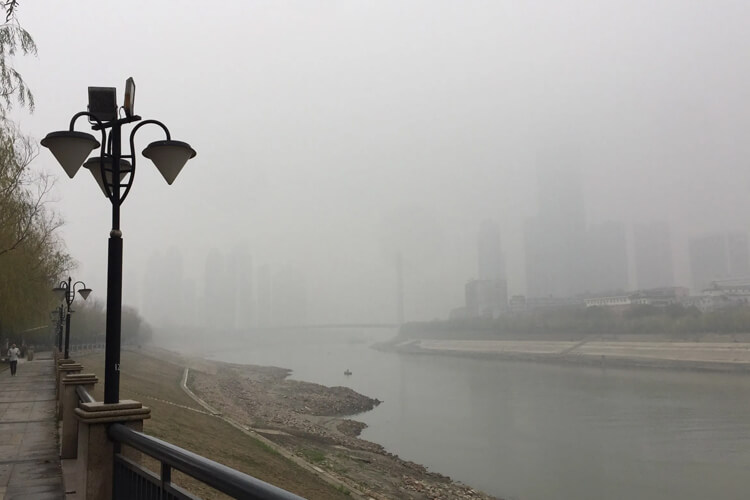

How to measure weather visibility?
There are usually two methods for measuring visibility: manual measurement and device measurement. Manual measurement has certain errors and is affected by different visual distances of each person. Therefore, the device monitoring method is more commonly used.
1. Visual observation
This method is one of the most commonly used methods to measure weather visibility. It uses the human eye to determine the weather visibility of the target object. The observer will estimate the distance and clarity of the target object based on visual perception. Or observe certain weather phenomena or some characteristics under specific weather conditions to determine the size of visibility. On rainy days, people can estimate weather visibility by observing the degree of obstruction of distant objects by raindrops. The advantage of this method is that it is simple and easy to use, and does not require the help of instruments or equipment. The disadvantage is that it is greatly affected by the subjective factors of the observer and is prone to errors.
2. Visibility sensor
The visibility sensor is based on the principle of scattering. Scattering means that when light passes through a certain substance, it is reflected and scattered by tiny particles, thus propagating in all directions. In the air, some suspended particles such as water droplets, smoke, aerosols, etc. will scatter visible light, thereby affecting the propagation of light. When a large number of particles gather together, fog or haze will form. At this time, people’s naked eyes cannot see the objects in front clearly, which means that people’s visibility is very low at this time.

When the visibility sensor is working, it will emit a beam of light, and then calculate the weather visibility by measuring the intensity of the reverse light after the light is scattered by the particles. As we all know, particles will scatter light. When light passes through a gas containing particles, the particles will scatter some frequencies in the visible light, resulting in a shortened distance for the light to propagate in the atmosphere, and people’s visibility will decrease. Generally speaking, the more particles there are, the lower weather visibility.
In the visibility sensor, the light sent interacts with the particles in the air. The light scattered by the particles is focused by a reflector and detected by the light sensor. Then, a computer algorithm is used to update the weather visibility value of the real-time environment. By measuring weather visibility in this way, people can understand the local weather conditions and take corresponding measures.
How does visibility affect weather?
Studies have shown that atmospheric particulate matter is an important factor affecting weather visibility. Moreover, visibility in foggy and hazy weather is much lower than that in sunny days, which is closely related to the concentration of atmospheric pollutants. Reduced visibility caused by condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere usually forms foggy weather. Reduced visibility caused by excessive concentration of particulate matter in the atmosphere usually forms haze weather. Reduced visibility caused by excessive dust in the atmosphere usually forms sandstorm weather. Therefore, in an environment with low visibility, it is usually accompanied by rain, fog, haze or sandstorm weather.
How does weather affect atmospheric visibility?
Factors that affect weather visibility include particle concentration, wind speed, humidity, temperature, etc.
1. Particle concentration
The concentration of pollutants and particles in the climate environment is a factor that directly affects weather visibility. There are many kinds of particles in the air, such as smoke, dust, etc. These particles will scatter and absorb light, thus affecting visibility. An increase in particle concentration will lead to a decrease in visibility. When there are more particles, light is easily scattered, making it difficult to see distant objects, thereby reducing weather visibility.
2. Wind speed
Wind speed will carry dust from the soil into the atmosphere to reduce weather visibility. When a sandstorm occurs, a large number of sand and dust particles are suspended in the air, causing the sky to become dim. In severe cases, it even makes the daytime like dusk, and weather visibility is greatly reduced.
3. Humidity
Atmospheric humidity refers to the content of water vapor in the air. An increase in humidity will lead to an increase in water vapor molecules in the atmosphere, thereby increasing the scattering of light in the air. When the humidity is high, water vapor molecules will scatter light, blurring distant objects and reducing weather visibility.
4. Temperature
An increase in temperature will lead to intensified atmospheric convection, thereby increasing turbulence in the air. Turbulence makes it easier for particles in the atmosphere to be suspended and dispersed, thereby reducing weather visibility. Therefore, in a high temperature environment, it will lead to low visibility.

In addition to the above factors, there are some other factors that will affect weather visibility. For example, weather conditions such as haze, rain, and snowfall will affect visibility. Water vapor will increase the concentration of particles in the air, thereby affecting visibility. Rain and snow will interfere with the propagation of light and also reduce visibility.
What are the main differences between fog, mist, and haze?
Fog, smog, mist and haze are different forms of pollutants in the atmosphere, and there are the following differences between them:
1. Fog: Fog is an aerosol system composed of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air near the ground. It mainly occurs in the air close to the surface, usually formed under conditions of low temperature and high humidity. The color of fog is mostly white, and visibility is low.
2. Mist: Mist is a thinner fog with a smaller particle diameter, generally below 10 microns. Mist has a strong scattering ability, making the sunlight appear blue.
3. Haze: Haze is an aerosol system composed of a large number of tiny particles (such as PM2.5) suspended in the air near the ground. The color of haze is gray or yellow, and visibility is low. The particles in haze mainly come from primary pollutants emitted by pollution sources such as cars and factories.
In summary, fog and mist are mainly composed of water droplets or ice crystals, with lighter colors and lower weather visibility. Haze is mainly composed of primary and secondary pollutants, with darker colors and lower weather visibility. Among them, smog is a secondary pollutant generated by photochemical reactions, while haze is an aerosol system composed of particulate matter.