Gardening is a thought-provoking and enjoyable activity. Sometimes, it’s not easy to figure out exactly how much water each plant needs. This is because different plants have varying moisture requirements depending on factors like how and where they are grown, and the type of soil they are in. Ultimately, watering plants is a science, you need to keep experimenting and learning from mistakes to master it. You have to be mindful of overwatering your plants, as well as ensuring they don’t lack water. Only by understanding the soil moisture in detail can you water your plants scientifically.
How does soil moisture affect plant growth?
We all know that plant roots absorb water from the soil to ensure growth and development, but both excessively high and low soil moisture can affect plant growth. When soil moisture is too low, it fails to meet the water needs of the plant, leading to dehydration and wilting. On the other hand, when soil moisture is too high, it blocks air from reaching the soil gaps, preventing the plant roots from breathing, which leads to oxygen deprivation and root rot. Therefore, only by maintaining an appropriate level of soil moisture can plants grow strong and healthy.
Top three ways to measure soil moisture
1. Observation method
We can roughly judge the soil’s moisture state by directly observing it with our eyes. This is because dry and moist soils differ in color, texture, and the growth condition of plants. For lawns, potted plants, and gardens, we can make an initial assessment of soil moisture by observing and touching it.
Color judgment: Moist soil typically has a darker color, ranging from dark brown to black, while dry soil tends to be lighter, closer to a yellowish or grayish-white color. However, it’s important to note that different types of soil naturally have different colors, so this method should be used in combination with other methods for better accuracy.

Texture sensation: First, use your finger to touch the soil surface. Moist soil will feel somewhat sticky and have a finer texture, while dry soil will feel loose and have a noticeable graininess. Next, gently press down on the soil with your finger. If the soil quickly returns to its original shape, it indicates that the soil moisture is good. If the soil remains indented and does not return to its original form, it suggests that the soil is quite dry. Finally, gently insert your finger about 5 cm below the surface of the soil (this depth typically reflects the main root zone of plants). Then, feel the texture and moisture level of the soil. If your finger easily slides into the soil and it feels moist but not sticky, the moisture level is suitable for plant growth. If it’s difficult to insert your finger, and the soil feels hard or dry, the soil needs watering. If the soil is overly wet and water seeps out, the moisture level is too high, and drainage or ventilation is needed.
Plant growth condition: The growth condition of plants is also an important indicator of soil moisture. If the leaves are wilting, drooping, or discolored, it is likely that the soil is too dry. On the other hand, if the leaves are overly lush, bright green, but the plant is not thriving, this could be a sign of excessive moisture in the soil, leading to oxygen deprivation in the roots.
2. Weighing method
Compared to the observational methods above, the weighing method for determining soil moisture is more precise. By comparing the weight differences of soil in dry and moist states, we can accurately calculate the soil’s moisture content. The specific steps are as follows:
Preparation: First, you will need a precise digital scale and a clean container (such as a plastic or ceramic bowl).
Sampling and weighing: Take a consistent sample of soil from the area you want to test and place it into the container. Weigh the container with the soil and record the weight as the “wet weight.”
Drying process: You can place the container with the soil sample in a well-ventilated area to dry naturally until the soil has lost all moisture. This process may take several days, depending on the soil’s moisture content and drying conditions. Alternatively, you can speed up the drying process by heating the soil or placing the container in an oven.
Weigh again: Once the soil is completely dry, weigh it again and record this weight as the “dry weight.”
Calculate moisture content: By comparing the “wet weight” and “dry weight,” we can calculate the soil’s moisture content. The calculation formula is:
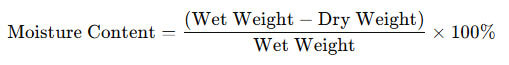
Notes: While this method is more accurate, it is also more time-consuming and requires the soil to dry completely. Therefore, in practical applications, we typically combine this method with the observational techniques to improve efficiency in determining soil moisture.
3. Soil moisture sensors
With the advancement of technology, soil moisture meters have become essential tools for determining soil moisture levels in home gardening and agricultural production. By measuring physical parameters like soil conductivity or resistivity, soil moisture meters can accurately reflect the water content in the soil.
Choosing a soil moisture meter: There are various types of soil moisture meters available on the market, including analog, digital, and smart models. Depending on your personal needs and budget, you can choose the right one for you. Here are some recommendations:
- For occasional measurements in your garden or potted plants, we recommend our portable soil moisture meter.
- For setting up a complete automatic irrigation system, we suggest our soil moisture sensor.
- For agricultural experts who wish to monitor soil moisture changes in a specific area over time, we recommend our multi-depth soil moisture sensor. It allows continuous monitoring of moisture changes at different depths.
- Additionally, there are specialized instruments such as the soil tensiometer, pH sensor, soil heat flux plate and 4-in-1 soil sensor to meet your varying needs.
Usage instructions: Before use, carefully read the user manual of the soil moisture meter to understand its operating principles and how to use it. To measure soil moisture, insert the probe into the soil to a certain depth (generally recommended to be 5-10 cm below the surface). Wait a few seconds for the reading on the display to stabilize, and then record the data.
Data interpretation: Different brands and models of soil moisture meters may have different reading ranges and units (such as percentage, voltage, or resistance values). Therefore, when using the device, be sure to refer to the manual for the correct range and unit instructions to interpret the data accurately.
Precautions: The accuracy of the soil moisture meter can be influenced by several factors, such as soil type, temperature, humidity, and the depth at which the probe is inserted. To improve the accuracy and reliability of your measurements, try to maintain consistent measurement conditions during use.
What should I do if my soil is too dry or too wet?
Solutions to high level soil moisture
If the soil moisture is too high, the first thing you should do is stop watering. Continuing to water according to your usual schedule will undoubtedly put more stress on the plants. Secondly, for potted plants or greenhouses, you can increase light exposure and improve ventilation to speed up the evaporation of moisture in the soil. Lastly, you can add organic matter and materials with good aeration properties, such as charcoal or perlite, to the soil to enhance its permeability and water absorption.
As mentioned earlier, excessive soil moisture primarily affects root respiration. Therefore, without damaging the root system, loosening the surrounding soil at a deeper level can help accelerate soil moisture evaporation and facilitate plant respiration.
Solutions to low level soil moisture
Proper watering is an essential way to replenish soil moisture. We should consider the plant’s needs and seasonal changes, adjusting the frequency of watering accordingly. Using methods like drip irrigation or sprinklers ensures that the water can fully penetrate the soil.
If you are outdoors and don’t have tools to measure soil moisture, how can you quickly determine the soil moisture? Don’t worry, here’s a simple trick:
First, collect a soil sample from the main root zone (40-60 cm deep). Then, take a portion of the sample and try to form it into a ball by hand. If the soil cannot be formed into a ball, it indicates that the moisture level is low, and watering is needed.
If the soil can form a ball, hold the ball at chest height and let it fall naturally to the ground (just let go, don’t throw it hard.). If the ball falls without breaking apart, it indicates that the soil moisture is high, and no watering is needed. If the ball falls apart, this suggests the soil is in an ideal state—well-drained and not lacking moisture. In this case, you can either water lightly or skip watering until the next scheduled time.
How to maintain soil moisture?
Adding mulch
During the hot summer months, you can spread a layer of mulch such as plastic film, straw, pine needles, or other organic materials on the soil surface. This layer acts as a protective barrier, effectively blocking direct sunlight and wind, which helps reduce soil moisture loss.

Improving soil
You can improve soil moisture retention by adding organic materials such as organic fertilizers, leaf mold, or peat. These substances enhance the soil’s ability to retain moisture. Additionally, incorporating materials like sand or clay can adjust the soil’s texture, improving both water retention and drainage. However, it’s important not to over-add these materials, as excessive amounts may hinder plant respiration and water absorption.
Timely watering
Proper and timely irrigation is an essential method for replenishing soil moisture. You can use methods such as seepage irrigation, drip irrigation, or sprinkler systems to reduce water evaporation and loss. Watering should be based on the plant’s needs and the soil’s moisture levels, ensuring water is applied at regular intervals and in appropriate amounts to avoid waste and prevent excessive dryness.
Using moisture retainers
Moisture retainers are materials that absorb water and release it gradually. You can sprinkle moisture-retaining agents on the soil surface or mix them into the soil to help maintain moisture levels. Common moisture retainers include crystal granules, natural clays, or liquid moisture-retaining agents. These materials help regulate soil moisture by absorbing excess water and releasing it when the soil dries out.