What is an infrared motion detector?
All living beings and objects on Earth emit infrared light of different wavelengths. An infrared motion detector works by detecting these varying wavelengths of infrared radiation to determine the movement of objects. Infrared detection technology converts invisible infrared radiation into measurable signals. Infrared motion detectors are widely used in various scenarios, including home security, commercial premises, and public facilities, to enable automatic alarms and monitoring functions.
| Renke Motion Detectors Recommend | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Types | Infrared motion detector | Microwave motion detector | Infrared + microwave detector |
| Photos |  |  |  |
| Sensor | PIR pyroelectric element | 24GHz millimeter wave radar | PIR pyroelectric element and 24GHz millimeter wave radar |
| Monitoring | Passive detection uses pyroelectric elements to detect infrared rays emitted by the human body. When the element receives infrared radiation, it will release electric charge and generate an alarm after detection and processing. | Active detection uses the Doppler effect to detect mobile signals. It detects whether there are moving objects by changing the frequency of the transmitted waves, and can detect subtle movements of the human body. | Using microwave detectors and human pyroelectric infrared sensors, the alarm signal will only be issued when both detectors detect human activities in the monitored area. It has super high detection and anti-false alarm performance. |
| Features | Low cost and good stability | Sensitive, strong penetrating, not affected by smoke, heat source, airflow | Sensitive sensing, stable performance, high recognition accuracy, and low misjudgment rate |
| Price | $21 | $27.9 | $29.4 |
| Inquiry | Contact us for detailed manual | ||
How does an infrared motion detector work?
Any object above absolute zero emits infrared radiation, with higher temperatures corresponding to shorter peak wavelengths of infrared emission. Infrared motion detectors operate by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by human bodies. They collect external infrared radiation and focus it onto an infrared sensor. These sensors typically use pyroelectric elements, which generate an electric charge when they detect changes in infrared radiation caused by temperature variations. After processing the signal, the detector triggers an alarm.
Types of infrared motion detectors
Classification by working principle
1. Passive Infrared Detector (PIR)
The principle of a Passive Infrared Detector is based on the temperature difference between a moving target and the surrounding environment. When a person enters the detection area, the infrared-sensitive components can detect the difference in temperature, triggering an alarm.
Why is it called “passive”? Because the detector itself does not emit any energy; it simply passively receives infrared radiation from the environment. Once installed, the detector adapts to the environment within seconds. If no person or animal enters the detection area, the infrared radiation in the scene remains stable. Passive infrared motion detectors can form detection zones that typically extend up to several tens of meters.
2. Active Infrared Detector (AIR)
An Active Infrared Detector operates by emitting infrared light and detecting its reflected signal to identify the presence of a target object. It actively projects a beam of infrared light, and when the beam encounters an object, part of the light is reflected back. By receiving this reflected light, the detector determines the presence of an object.
Since this type of detector actively emits light, it can function normally in complete darkness and is not affected by ambient light conditions.
Differences Between Passive Infrared Detectors (PIR) and Active Infrared Detectors (AIR)
| Aspect | Passive Infrared Detector (PIR) | Active Infrared Detector (AIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Does not emit infrared light; detects changes in ambient infrared radiation. | Emits and receives infrared beams to detect moving objects. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost. | Typically higher cost. |
| Installation | Easy to install. | Requires precise alignment of transmitter and receiver, making installation more complex. |
| False Alarm Rate | May generate false alarms due to moving objects like wildlife. | Usually has a lower false alarm rate. |
| Environmental Adaptability | Highly adaptable to environmental changes. | Strong resistance to environmental interference. |
Classification by detection range and accuracy
Wide-Angle Infrared Detector
A wide-angle infrared detector is a device designed to detect infrared radiation across a broad field of view. It can monitor a larger area, making it suitable for spaces like living rooms or entryways.
Narrow-Beam Infrared Detector
A narrow-beam infrared detector is a highly directional infrared sensor designed to detect infrared radiation within a specific directional range. Compared to standard infrared detectors, narrow-beam detectors have a smaller Field of View (FOV), allowing for more precise detection of signals from a particular direction while minimizing interference from surrounding environments. This characteristic makes them particularly valuable in applications requiring high sensitivity or high resolution.
Classification by technology
Microwave + Infrared Dual-Technology Detector
The microwave + infrared dual-technology detector is a security device that combines two detection methods: infrared and microwave. When in operation, it simultaneously detects two signals: the intruder’s temperature (via infrared sensing) and movement (via microwave detection). This dual-signal approach significantly reduces the false alarm rate, making it more reliable than single-technology detectors. Its false alarm rate is only 1/421 compared to single-technology detectors and 1/270 compared to other dual-technology detectors, which makes it widely used in various engineering projects.
AI-Enhanced Infrared Motion Detector
The AI-enhanced infrared motion detector integrates traditional infrared motion detection technology with artificial intelligence algorithms, significantly improving detection accuracy. By using edge AI chips, it can analyze infrared signals in real time and filter out irrelevant information such as wind or moving leaves. This advanced capability makes it highly suitable for applications in smart homes, security surveillance, and industrial monitoring, offering broad development potential across various fields.
How to install the infrared motion detector?
Example: RS-HW-N01-EX RS485 ceiling-mounted infrared motion detector wiring diagram
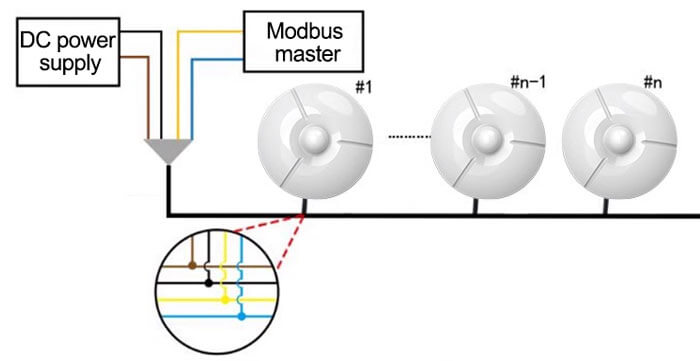
| Line color | Instruction | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Brown | Power positive | 10-30V DC |
| Black | Power negative | |
| Yellow | 485-A | — |
| Blue | 485-B | — |
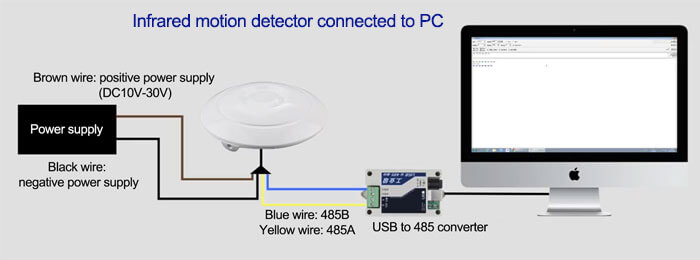

General installation principles for infrared motion detector
The infrared motion detector installed indoors are used to detect unauthorized personnel entering. To prevent false alarms caused by pets, small animals, etc., the sensor should generally be positioned at least 50 cm above the ground. The shutter time should be set to a faster position to quickly respond to illegal intrusions.
The infrared motion detector installed on outdoor perimeter walls mainly function to prevent malicious climbing. Both top and side mounting options are possible. For top-mounted infrared motion detectors, they should be positioned 25 cm above the top of the fence or wall to reduce false alarms caused by small animals like birds or cats moving on the wall. Four-beam detectors have better false alarm prevention than two-beam detectors, and two-beam detectors are better than single-beam detectors. Side-mounted detectors should also be installed as close to the top of the wall as possible. Infrared motion detectors are usually wall-mounted, so they are mostly installed on the exterior to avoid interference from small animals like birds or cats. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and users should choose according to the characteristics of their building and anti-theft requirements.
How to avoid false alarms with infrared motion detectors?
The ideal infrared motion detector should only respond to the presence of humans and not to the movements of animals like dogs, cats, or mice, nor should it react to changes in the indoor environment such as temperature, humidity, wind, rain, sound, or vibrations. Achieving this is not easy, and most devices not only respond to the presence of humans but are also affected by various irrelevant factors.
A false alarm occurs when an alarm is triggered without any actual intrusion. False alarms can be caused by component malfunctions or environmental factors, and their consequences can be severe. The mildest consequence is that they cause unnecessary inconvenience, leading to frustration and significantly reducing the reliability of the alarm system. The worst-case scenario is that false alarms prompt police or security personnel to rush to the scene unnecessarily, endangering their own safety and the safety of others nearby. Therefore, false alarms are a critical weakness of alarm systems.
Let’s analyze the main causes of false alarms in infrared motion detectors:
Poor anti-interference ability
Infrared motion detectors with weak anti-interference capabilities are prone to false alarms due to interference from other devices operating on the same frequency, or because of inaccurate detection of intrusion behavior.
Susceptibility to environmental factors
The infrared motion detector is easily affected by environmental factors like temperature and light, which can lead to false alarms.
Repeated codes from wireless systems
If both the main unit and the detector use wireless encoding and there is a coding conflict or overlap, it can cause a false alarm due to signal interference between the devices.
Poor quality of the alarm system
Low-quality alarm systems, such as those with defective components or poor manufacturing processes, can result in false alarms.
Improper installation
If the infrared motion detector is not installed correctly—such as with incorrect angles or positioning—false alarms can occur due to poor setup.
Environmental and human factors
Environmental factors like air movement, pet activity, or human error (such as incorrect operation, accidentally triggering the alarm, or mistakenly entering a secured area) can also cause false alarms.
There are many complex and varied reasons that cause false alarms. Therefore, to reduce false alarms in infrared motion detectors, it is crucial to consider multiple factors. This includes selecting detectors based on both technical and performance criteria, such as the design of the Fresnel lens, the microprocessor programming, multi-sensor technology, automatic rolling code technology, manufacturing processes, usage methods, temperature compensation, and adjustments to sensitivity and detection range. These combined factors determine the detector’s performance and false alarm rate. Additionally, choosing a reputable sensor brand and ensuring proper installation can significantly reduce false alarms.