A sensor is a device that can sense the measured information and transform it into an electrical signal or other required forms of information output according to a certain rule to meet the requirements of information transmission, processing, storage, display, recording, and control. With the development of the Internet of Things technology, sensors are gradually applied to more and more industries such as agriculture and industry.
Agriculture sensors such as air temperature and humidity, soil moisture, soil pH, light intensity, and carbon dioxide are often used to collect data in all aspects of crop growth such as nursery, growth, and harvest. Agricultural conductivity and agricultural pH sensors are used to monitor water and fertilizer. The mixed fertilizer liquid in the integrated monitoring system is monitored.
What are agricultural sensors?
Agricultural sensors mainly include plant information sensors and environmental sensors. Plant information sensors detect the growth and development characteristics of plants during their growth process, digitally process plant growth signs, and then analyze plant growth conditions. Environmental sensors mainly monitor and analyze the environment in which plants grow, such as water, soil, and air, to understand environmental changes and ensure that the plant growth environment reaches the optimal level. At present, commonly used agricultural sensors mainly include temperature sensors, humidity sensors, pH sensors, gas sensors, biosensors, photoelectric sensors, and pressure sensors.
List of agriculture sensors
Sensors are the foundation. The application of IoT technology can collect information about plants and animals and keep track of their dynamics in real time. Sensors will play an indispensable role in agricultural production. Fertilization, spraying, irrigation and other links all require sensor data collection. By monitoring the soil, pests, humidity and other data of plants, it is possible to determine when to fertilize, spray and irrigate, thus avoiding the waste of resources and environmental damage based on traditional experience.
1. Temperature and humidity sensor
The air temperature and humidity sensor can monitor the air temperature and humidity changes in the agricultural planting environment. The default temperature and humidity monitoring ranges are -40℃~+80℃ and 0%RH~100%RH respectively. The wall-mounted enclosure can be wall-mounted in greenhouses, etc. A shading place with good air circulation in the environment; during outdoor monitoring, it can be installed in a solar radiation shield for outdoor weather monitoring together with the agrometeorological station. Renke temperature and humidity sensor adopts a temperature and humidity measurement unit imported from Switzerland and a built-in industrial-grade imported US The microprocessor chip has the characteristics of accurate measurement and stable communication.

2. Soil moisture sensor
The soil moisture sensor is one of the most important agricultural sensors. Soil moisture determines the water supply status of crops. Too high or too low soil moisture will affect the normal growth of crops above the ground. Only with suitable soil moisture, root water absorption and leaf transpiration can reach a balanced state, thereby promoting crop root growth. The Renke soil moisture sensor measures the volume percentage of soil moisture by measuring the dielectric constant of the soil. The soil moisture tester method that meets the current international standards can directly and stably reflect the true moisture content of various soils.

3. Soil PH sensor
Maintaining proper soil pH is the basic requirement for normal crop growth. When the Renke soil pH sensor detects the electrode (sensor) directly contacts the soil, the current generated by the oxidation-reduction reaction in the chemical reaction is used, and the current value will drive the data of different pH value units corresponding to the ammeter, which is converted by the host. The results are displayed in the form of numerical values; the steel needle is a special anti-corrosion electrode made of special alloy material, which is resistant to acid and alkali corrosion. The shell is completely sealed with black flame-retardant epoxy resin, and the protection level is IP68.
4. Light sensor
The light sensor includes three parts: transmitter, receiver, and a detection circuit. All of them are composed of electronic parts. It does not include mechanical working time. It can quickly monitor the light intensity of 0 to 200,000 Lux with a very short response time. The application of light sensor in greenhouse agricultural planting can help growers to accurately grasp the sunshine time law, light saturation point, and light compensation point of plant growth, and then adjust their light preferences through manual control technology to control and improve The scientific growth of crops in order to achieve high yields.

5. CO2 sensor
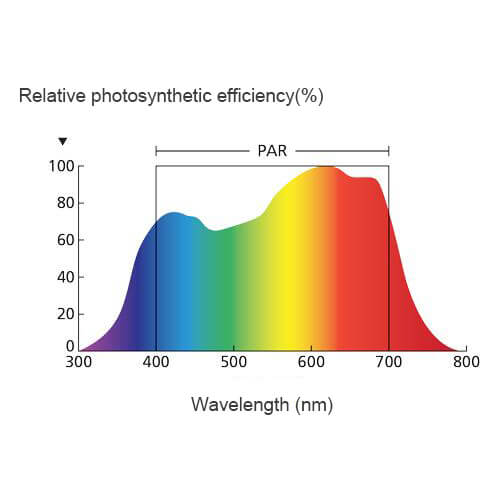
Crops continuously absorb CO2 in the atmosphere for photosynthesis and use photosynthesis to produce nutrients to maintain the development and growth of crops. Studies have found that when the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide increases, the photosynthesis of plants will be greatly enhanced. Renke carbon dioxide sensor uses a new infrared verification technology to measure the CO2 concentration in the environment. The response is quick and sensitive, avoiding the life and long-term drift of traditional electrochemical sensors; the default measurement range is 0~5000ppm, with temperature compensation, which is affected by external Temperature influence is small.

6. Barometric pressure sensor
Barometric pressure sensor can measure the change of air pressure. Farmers can use barometric pressure sensor to understand the change of weather, including the drop of air pressure and the change of wind speed, so as to do a good job of disaster prevention and reduction of crops in time. For example, when it is predicted that the air pressure will continue to drop in the next period of time, farmers can harvest mature crops in advance to avoid losses caused by weather disasters.
7. Rain gauge
Rain gauge is a sensor used to monitor precipitation. Rainfall and snowfall are effective ways for nature to replenish soil moisture. The commonly used outdoor tipping bucket rain gauge has accurate measurement and small error. It can be used with evaporation sensor to analyze soil moisture more accurately. Rain gauge is a tool for monitoring precipitation and precipitation frequency in agricultural sensors, providing important data for irrigation management.
What are the benefits of agriculture sensors?
Control irrigation system: By measuring soil moisture and ambient humidity, as well as weather data monitored by weather stations, soil moisture can be accurately determined. Sufficient water can be added to the soil in a timely manner. For example, Renke multi-layer soil sensor can be used to connect irrigation systems to achieve automated irrigation, and the timing and amount of irrigation can be controlled through programs on mobile devices.
Conduct pest and disease monitoring: Deploy some insect traps and pesticide sprayers in the farmland. Sensors can monitor the temperature, humidity, air pressure and other data in the area in real time, so as to better control pests and diseases in the farmland. For example, the insect monitoring instrument is equipped with a meteorological sensor, and growers can choose the right insecticide based on these monitoring data.
Optimize fertilizer management: By measuring the concentration of dissolved oxygen, metal ions, and hydrogen ions in the soil, we can better understand the condition of the soil, grasp the nutritional needs of crops, and provide better fertilizer management. For example, using a water-fertilizer machine to monitor soil nutrients and automatically replenish fertilizers can help farmers maximize fertilizer use and reduce waste.
Improve planting efficiency: Sensors can be used to understand meteorological data and scientifically manage and maintain crops during their growth. For example, sensors used to measure the light intensity and temperature of plants are effective in different weather and microclimate conditions, and understand and control the growth environment of crops, thereby optimizing the production efficiency of crops.
Promote sustainable development: Agricultural sensors can also help farmers accurately calculate land utilization, reduce agricultural wastewater and waste gas emissions, reduce environmental impact, and provide support for achieving sustainable development.
Agricultural sensors are mainly used in agricultural monitoring with the water and fertilizer integrated machine system. They are mainly used to monitor the conductivity, pH, and temperature values of the fertilizer liquid after mixing and mixing, and display and upload to the water and fertilizer control system through the LCD screen. The built-in memory chips of agricultural conductivity and agricultural PH sensors have storage functions, which can store historical data of 2 days and 3 days respectively, adopt high-precision AD conversion and single-chip micro-processing technology, and have multiple functions such as data acquisition and automatic temperature compensation.
Compared with modern agriculture, traditional agriculture, which relies on a lot of manpower and uses simple agricultural tools and machinery, has gradually shown its disadvantages. Modern agriculture uses the Internet of Things and sensor technology to provide accurate and timely crop growth data for formulating scientific planting programs, saving labor, optimizing crop varieties, and improving crop quality and yield.