Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless gas that is widely present in the atmosphere. In the natural world, the levels of carbon dioxide are always in a dynamic equilibrium of continuous growth and consumption. Indoors, carbon dioxide tends to accumulate more easily compared to outdoor environments. Indoor carbon dioxide gas primarily originates from daily human activities. For example, each person releases approximately 1 kg of carbon dioxide per day through respiration, the average use of a computer indirectly emits 10.5 kg of carbon dioxide over a year, and processes like heating and packaging frozen food also contribute to carbon dioxide emissions. Carbon dioxide detectors can display the indoor CO2 levels and remind users to ventilate the space promptly.
Carbon dioxide detectors monitor carbon dioxide levels to improve air quality. They are also used in homes, offices and classrooms to measure indoor air quality. Common applications for CO2 detectors include monitoring IAQ, process control, indoor greenhouses, bars, restaurants, breweries and landfills.
How does a carbon dioxide detector work?
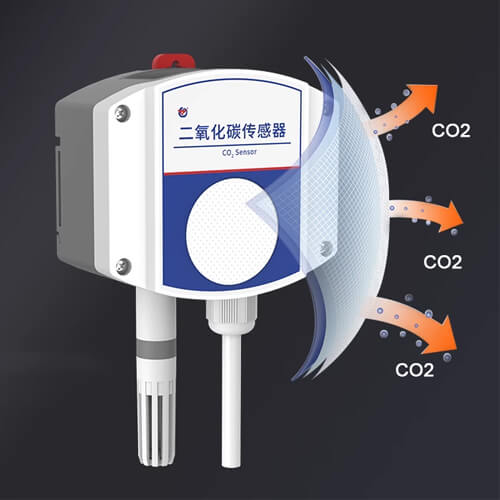
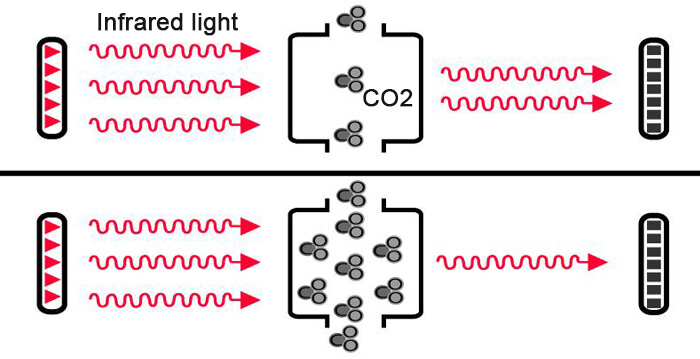
Carbon dioxide detectors operate based on the absorption of infrared light to detect the presence of CO2 molecules in the air. Carbon dioxide gas molecules can absorb a specific wavelength of infrared light while allowing other wavelengths to pass through. When infrared light passes through an air sample chamber, the amount of absorbed infrared light is directly proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide. Therefore, the more carbon dioxide gas present, the more infrared light is absorbed. Carbon dioxide detectors calculate the concentration of CO2 by measuring the amount of infrared light that reaches the filter on the detector.
Where does carbon dioxide come from?
Carbon dioxide gas comes from two aspects, one is human activities (including burning fossil fuels, deforestation), and the other is natural phenomena (including volcanic eruptions, animal and plant respiration, and decay of animal and plant corpses).
Why do we need carbon dioxide detectors?
Improve indoor air quality
The level of indoor carbon dioxide concentration is also a criterion for judging the quality of air. Excessive carbon dioxide concentration indicates poor indoor ventilation, making residents feel suffocated and listless if they stay in this environment for a long time. In addition, excessive carbon dioxide concentrations can lead to an increase in various anaerobic bacteria and viruses. Because of poor air quality, viruses, bacteria and particulate matter are more active. Installing carbon dioxide detectors indoors to monitor indoor carbon dioxide levels can remind residents to open windows for ventilation and improve indoor air quality.
Improve production safety
In industrial activities, there are some places where carbon dioxide detectors must be installed, such as where carbon dioxide is produced, used or stored. Although carbon dioxide gas itself is not toxic, an environment with excessive carbon dioxide can have negative effects on workers' bodies. For example, long-term lack of oxygen can lead to headaches or suffocation. Therefore, in order to ensure the safety of the workplace, it is necessary to install a carbon dioxide concentration detector to monitor carbon dioxide levels in a timely manner and take appropriate preventive and control measures.
Protect environment
From an environmental protection perspective, CO2 is a greenhouse gas, and elevated concentrations can lead to global temperature increases, exacerbating the effects of global warming. Therefore, environmental protection organizations or agencies need to equip themselves with carbon dioxide detectors to monitor CO2 levels and minimize CO2 emissions as much as possible in order to protect the environment.
Where should I place a carbon dioxide detector?
Depending on the place of use, the installation methods are also different:
- Office or Classroom: Mount the CO2 detector approximately 12 inches (30 cm) above the floor with no obstructions around the device.
- Home: The installation location of the indoor carbon dioxide detector is not so strict. You can put it on the bedside table or the living room table. If you want accurate measurements, mount the detector 36 to 60 inches (90-150 cm) above the ground.
- Laboratories, hospitals, factories: Install carbon dioxide detectors away from hazardous materials and fuels, with no obstructions around them.
Are there different types of carbon dioxide detectors?
There are various types of carbon dioxide detectors on the market depending on the place of use and working principle. You can choose the appropriate carbon dioxide detector according to your needs.
What is the difference between CO2 and CO detectors?
Carbon monoxide (CO) gas and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas are indeed two entirely different gases. Carbon monoxide is toxic, has an irritating odor, and is flammable. Carbon dioxide is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, does not support combustion, and is even used in fire extinguishers. While carbon dioxide can naturally exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, carbon monoxide does not.
Carbon dioxide detectors do not detect CO, and CO detectors do not detect CO2. Carbon dioxide detectors typically use infrared sensors to detect gas levels in the atmosphere, while carbon monoxide detectors primarily use electrochemical sensors, gel sensors, and metal oxide semiconductor sensors.
The densities of the two gases are also different. Carbon dioxide from a gas cylinder leak is denser than air, so carbon dioxide detectors should be placed near the floor. Carbon monoxide has a density similar to that of air, so CO detectors should be placed at a higher level.
How long does a CO2 detector work?
The most gas sensors’ lifespan depends on the quality of the internal measuring unit and the working environment.
For carbon dioxide detectors, the lifespan is primarily dependent on the core component, which is the sensor. Electrochemical sensors, commonly used in CO2 detectors, typically have a lifespan of around 2-3 years. This is because the electrolyte within the sensor naturally depletes over time during sensor use, and even if not in use, it will still degrade. Therefore, there is usually a fixed replacement cycle, and the sensor must be replaced once it reaches the end of its lifespan.
The most common carbon dioxide detectors typically utilize non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) sensors as their core technology. When used correctly, NDIR sensors can last for 5-10 years or more.
What are the recommended carbon dioxide levels in indoor air?
According to ANSES (the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety), the typical indoor air carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in buildings usually range from 350 to 2500 parts per million (ppm).
ANSES recommends adequate ventilation in schools and other public places to prevent CO2 levels from exceeding 1000 ppm. People feel uncomfortable when exposed to a carbon dioxide environment with a concentration of 1000 ppm. If they stay in such an environment for a long time, it will seriously damage their health. Therefore, it is necessary to follow the recommendations and control the carbon dioxide concentration within a reasonable range.
How to choose best carbon dioxide detectors?
Range
The measurement range of a carbon dioxide (CO2) detector is an important consideration when selecting one, but there is no need to pursue an excessively wide range. In the natural environment, the normal concentration of CO2 gas in the air is 0.04%, which is equivalent to 400 ppm (parts per million), and in densely populated urban areas, it might reach 500 ppm. In general, indoor CO2 concentrations above 5000 ppm can severely impact human health. Therefore, for indoor use, selecting a CO2 detector with a range of 0-5000 ppm should be sufficient.
Accuracy
Accuracy is usually one of the important criteria for measuring the reliability of a detector. A smaller number means the sensor has smaller errors. The value during the measurement process is more reliable. Generally, detectors with higher accuracy are more expensive.
Alarm
In some dangerous situations with strict requirements on carbon dioxide concentration, carbon dioxide detectors with real-time alarm functions are usually selected. Once the CO2 concentration in the environment exceeds the upper and lower limits, the detector immediately alarms and sends an email to notify the administrator. Minimize losses.
Installation
Choosing a carbon dioxide detector that is simple to install not only saves costs, but also saves time. In particular, multiple carbon dioxide detectors need to be installed at different locations, and multiple devices usually need to be connected to a unified monitoring host. In this case, a CO2 detector that is simple and easy to install is very important.
Display
Choose a carbon dioxide detector that can clearly display the value. You may be wondering, why is this function important? This is because many manufacturers on the market currently make the display screen of the detector difficult to read in order to reduce costs.