Agricultural irrigation mainly refers to irrigation operations carried out in agricultural farming areas. Agricultural irrigation methods can generally be divided into traditional surface irrigation, ordinary sprinkler irrigation, and micro-irrigation. Traditional surface irrigation includes border irrigation, furrow irrigation, submerged irrigation, and flood irrigation. However, this type of irrigation method often consumes large amounts of water and has low water utilization. It is a very unreasonable agricultural irrigation method. Besides, ordinary sprinkler irrigation technology is a common irrigation method in agricultural production. However, the water utilization efficiency of ordinary sprinkler irrigation technology is not high. Modern agricultural micro-irrigation technologies include micro-sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, and infiltration irrigation. These irrigation technologies generally have good water-saving performance and higher water utilization rates than traditional irrigation methods.
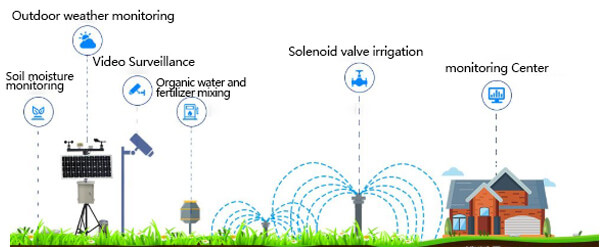
The implementation of a scientific automated irrigation system can save water resources and increase crop yields. The core of the automatic irrigation system is the using a soil moisture sensor to control irrigation. soil moisture sensor and automatic watering system can minimize water waste. This article provides methods and recommendations for automatic irrigation planning using soil moisture sensors.
At present, the main methods for measuring soil moisture on the market are the neutron attenuation method, tensiometer wet method, and rapid dielectric method.
Neutron soil moisture tester
The neutron attenuation method measures soil water content. Fast neutrons moving at high speeds can change direction and produce energy loss due to the interaction of materials with slow neutrons. The attenuation is also different due to different water content in the measured material. The main reason is the water contains hydrogen atoms, and the loss of neutrons to hydrogen atoms is much greater than the loss to other atoms. In this way, the soil water content can be determined by measuring slow neutrons, that is, the degree of attenuation can be used to determine the substance in the test. The neutron soil moisture tester is designed according to this principle.

he advantage of this method is that the speed is accurate, but the important thing is that if this method is not well-shielded, it is easy to cause radiation leakage, which will pollute the environment and endanger human health. It is especially difficult to measure the shallow soil moisture content, and the shallow soil moisture content Crop growth is closely related to changes in irrigation, rainfall, evaporation, etc. It is the most active part of soil moisture and requires real-time monitoring, which greatly limits the further popularization and application of the neutron method. The fence has been banned from use.
Dielectric soil moisture sensor
The dielectric soil sensor uses the dielectric properties of the soil to measure the soil moisture content, and it is also an effective, fast, simple, and reliable method. For a capacitive humidity sensor with a certain geometric structure, its capacitance is proportional to the dielectric constant of the measured material between the two poles. Since the dielectric constant of water is much larger than that of ordinary materials, when the moisture in the soil increases, its dielectric constant increases correspondingly, and the capacitance value given by the humidity sensor during measurement also increases. The corresponding relationship between the capacitance of the sensor and the soil water can measure the soil moisture.

Capacitive humidity sensors are characterized by high accuracy, a wide range, a wide variety of measurable materials, and a fast response speed, which can be applied to online monitoring to realize automated IJI pressure switches.
Soil water tension sensors
Tensiometer type soil moisture sensor is a kind of sensor that is widely and successfully used in some soil moisture measurement. This instrument has a porous porcelain head, which is connected to a vacuum gauge through a water-filled pipe. The device is inserted into a borehole in the soil. The porous porcelain head is closely attached to the soil, and the vacuum gauge is set on the ground. The use of tensiometers to measure soil moisture content has been greatly developed.
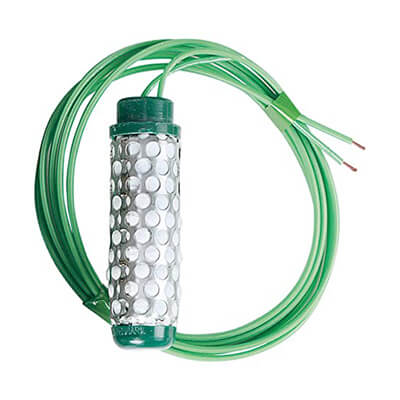

Its advantages are: the structure and principle are relatively simple, it can be measured online in real-time, and the flow direction and penetration depth of water in the soil can be determined, but its shortcomings are also very prominent. Its measuring range is largely affected by soil quality. For clay, due to its good air permeability, even when the negative pressure of soil moisture is lower than 0-8Pa, the soil moisture content can be measured with a tensiometer. This method measures the suction of soil water, which needs to be converted into soil water content according to the soil-water characteristic curve. Because the relationship between soil water and energy is very complex, nonlinear, and susceptible to many physical and chemical characteristics of the soil, even if it is the same day, this relationship is also very complicated, which makes it extremely difficult, inconvenient, and inconvenient to use tension to estimate soil moisture content, and brings large errors. This method has hysteresis and loopback, which affect its measurement speed. The existence of the above defects greatly restricts the popularization and application of electronic rulers of this method.
Automatic irrigation system using soil moisture sensor:
The soil moisture sensor can measure the frequency change caused by the sensor’s dielectric constant in the soil, and then transform it into a voltage or current relationship corresponding to the soil moisture content, to achieve accurate measurement of the volumetric moisture content of soil and other porous media. In simple terms, the soil moisture sensor has three stainless steel probes for inserting into the soil. The soil moisture sensor buried in the root of the crop monitors the moisture in the root-soil, and the sensor will monitor the results of “high humidity” and “low humidity” through the detection circuit. The “too low” signal is transmitted to the main controller through the encoder, and the main controller determines the control state. If the humidity is too high, the irrigation will be stopped; if the humidity is too low, the solenoid valve connected to the water source is controlled by photoelectric isolation and a relay. The system also has a fault alarm function. The main controller communicates with the host computer through the communication interface, which can monitor the operating status of the system in real-time or analyze historical data.
Working principle of automatic soil moisture sensor irrigation control
Automatic controlled irrigation is the use of soil moisture sensor in the field to collect or monitor soil information, field information, and crop growth information, and transmit the monitoring data to the head control center, and issue corresponding irrigation management instructions to the terminal under the corresponding system software analysis and decision.
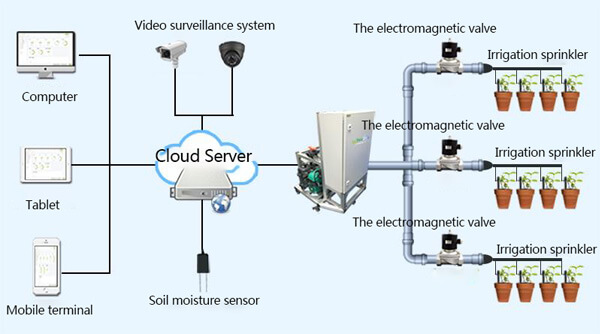
Components of an automated irrigation system
Monitoring Center:
Hardware: servers, computers, printers, large display screens, switches, etc. To
Software: water-saving irrigation system platform, database software, and operating system software.
Communications network:
GPRS/4G/Lora
Valve control system:
The valve monitoring system is composed of valve control, solenoid valve, and field controller.
The valve control system is to realize the water flow interception and distribution function for the farmland irrigation divisional operation pipe network. The system adopts a full wireless roaming network, and there is no need to lay lines in the field. It realizes the remote transmission of data through division management and cascade communication. Each solenoid valve has a special name. The solenoid valve is opened according to the plan made by the rotation irrigation. The monitoring center issues instructions to the designated solenoid valve or the rotation irrigation group to open the solenoid valve for watering, or close the solenoid valve to stop watering. According to the soil moisture content, the valve controller can be linked to realize automatic irrigation. The soil moisture value is set in the system. When the soil moisture is lower than the set value, the solenoid valve is opened for irrigation, and when the value is reached, the solenoid valve is closed to stop irrigation. The valve controller is connected to the solenoid valve through a cable, and the valve controller communicates with the field controller through wireless (Lora), and the switch valve command is sent to the valve controller by the field controller through the Lora communication method.
Soil moisture monitoring system:
The soil moisture monitoring system consists of a valve controller, a soil temperature and humidity sensor, and a field controller.
The soil moisture monitoring system mainly collects and processes soil moisture. It can be managed by an all-digital network platform, and the data collected by the front-end digital can be transmitted back to the control center and each monitoring center through the GPRS/4G network through the wireless communication terminal to realize the functions of distributed monitoring, centralized control, and management.
The soil temperature and humidity sensor is connected to the valve controller through a 485 cable. The valve controller communicates with the field controller through Lora, and the collected data is uploaded to the monitoring center by the field controller through the 4G network.
Water pump control system:
The water pump control system is composed of a motorized well controller, PLC, and water meter.
The water pump control system monitors the power consumption of the deep well submersible pump, the operation status of the pump unit, the pipeline flow, and other parameters, and transmits it back to the control center and each monitoring center through the GPRS/4G network to realize the functions of distributed monitoring, centralized control, and management.
Advantages of automatic irrigation system with soil moisture sensor
The automatic irrigation system realizes intelligent irrigation: as long as the irrigation program is set, it can be fully automatic operation, automatically closed on rainy days, and automatically opened on sunny days.
The automatic irrigation system realizes precise irrigation: the lawn, flowering shrubs, grass flowers, and moss are controlled in zones, and different irrigation procedures are set to meet the water requirements of different plants and realize precise irrigation management.
Automatic irrigation systems can save labor: in garden management, with this intelligent irrigation system, there is no need to water manually, and more time can be saved to take care of other details.
The automatic irrigation system achieves improved quality: precise intelligent irrigation management, and proper water and fertilizer management during the garden management period can make plants grow better. The microclimate created by automatic watering can wash away the dust of plant leaves and improve the living environment. When irrigating, the sprinkler irrigator has a variety of water features, which adds a dynamic landscape to the courtyard and enhances the quality of the garden.
The importance of agricultural automatic irrigation system
The application of agricultural automatic irrigation systems has changed human manipulation, randomness, and blindness of operation to a certain extent. It can not only increase the utilization rate of the source and alleviate the contradiction of increasingly tense water resources but also increase the output of crops and reduce the cost of agricultural products. The agricultural automatic irrigation system based on iot soil moisture sensor technology is the only way for the world to develop high-efficiency agriculture and precision agriculture.