Soil moisture sensors are also known as soil moisture meters. It is mainly used for measuring soil volumetric water content, monitoring soil moisture, agricultural irrigation, and forestry protection. The soil moisture sensor commonly used at present has FDR type and TDR type, namely frequency domain type, and time-domain type.
Types Of Soil Moisture Sensors
The most common types of soil moisture sensors include tensiometer, capacitance, dielectric method, gypsum blocks, volumetric, and neutron probes. These sensors either measure soil tension when placed in the soil or measure volumetric water content.
Soil moisture sensor for agriculture
The soil moisture sensor is a device that measures the current soil moisture. Sensors are integrated into irrigation systems in agriculture to help arrange water supply efficiently. Such meters help reduce or enhance irrigation to achieve optimal plant growth.
Capacitance
Using the dielectric properties of soil to measure soil moisture content is also an effective, fast, simple, and reliable method. For a capacitive soil moisture sensor with a certain geometric structure, its capacitance is proportional to the dielectric constant of the measured material between the two poles. Since the dielectric constant of water is much larger than that of ordinary materials, when the moisture in the soil increases, its dielectric constant increases correspondingly, and the capacitance value given by the humidity sensor during measurement also increases. The corresponding relationship between the capacitance of the sensor and the soil moisture can measure the soil moisture.

Capacitive soil moisture sensors are characterized by high accuracy, wide range, a wide variety of measurable materials, and a fast response speed, which can be applied to online monitoring to realize automated IJI pressure switches.
Tensiometer
Tensiometer soil moisture sensor is a kind of sensor that is widely and successfully used in some soil moisture measurements. This instrument has a porous porcelain head, which is connected to a vacuum gauge through a water-filled pipe. The device is inserted into a borehole in the soil. The porous porcelain head is closely attached to the soil, and the vacuum gauge is set on the ground. There is a great development in using a tensiometer to measure soil moisture content.

Its advantages are: the structure and principle are relatively simple, it can be measured online in real-time, and the flow direction and penetration depth of water in the soil can be determined, but its shortcomings are also very prominent. Its measuring range is largely affected by soil quality. For clay, due to its good air permeability, even when the negative pressure of soil moisture is lower than 0-8Pa, the soil moisture content can be measured with a tensiometer. This method measures the suction of soil water, which needs to be converted into soil water content according to the soil-water characteristic curve. Because the relationship between soil water and energy is very complex, nonlinear, and susceptible to many soil physical and chemical properties.
Neutron
Neutron moisture determination method. The neutron source is inserted into the soil to be tested through the probe tube, and the fast neutrons it continuously emits collide with various elements in the soil and lose energy, thereby slowing it down. Among them, when fast neutrons collide with hydrogen atoms, they lose the most energy and are easier to slow down. Therefore, the higher the water content in the soil, that is, the more hydrogen atoms, the greater the cloud density of slow neutrons.
By measuring the correlation between the density of the slow neutron cloud and the soil moisture content, the moisture content in the soil can be determined, and the measurement error is about ±1%. The neutron instrument method can periodically and repeatedly measure at different depths in the original position, but the vertical resolution of the instrument is poor, and the surface measurement causes large errors due to the easy dissipation of fast neutrons in the air. Therefore, a special type is designed Neutron instrument, or use shielding, or use other methods to calibrate.
FDR and TDR
The time-domain reflectometer msethod refers to the method of calculating the soil moisture content by measuring the dielectric constant of the soil, which is abbreviated as the TDR method. Since the dielectric constant of water in the soil is much greater than the dielectric constant of solid particles and air in the soil, as the soil moisture content increases, the dielectric constant value increases, and the propagation speed of electromagnetic waves in the medium are proportional to the dielectric constant. The square root is inversely proportional, so the electromagnetic wave propagation time along the waveguide rod is also extended. By measuring the propagation speed of high-frequency electromagnetic pulses in the soil along the waveguide rod, the soil moisture content can be determined.
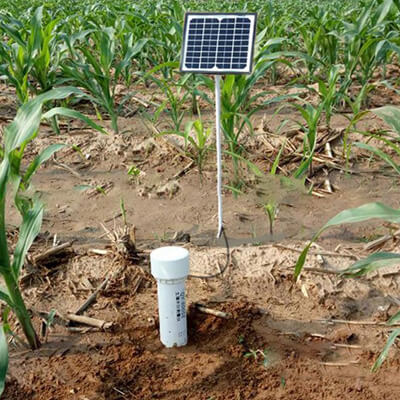

The frequency-domain soil moisture sensor method is abbreviated as FDR. It uses the principle of an electromagnetic pulse to measure the apparent permittivity (ε) of the soil according to the propagation frequency of electromagnetic waves in the medium to obtain the soil volumetric water content (θv). After the soil is calibrated, the measurement accuracy is high, and the shape of the probe is not limited, and multiple depths can be measured at the same time, which makes data acquisition easier.