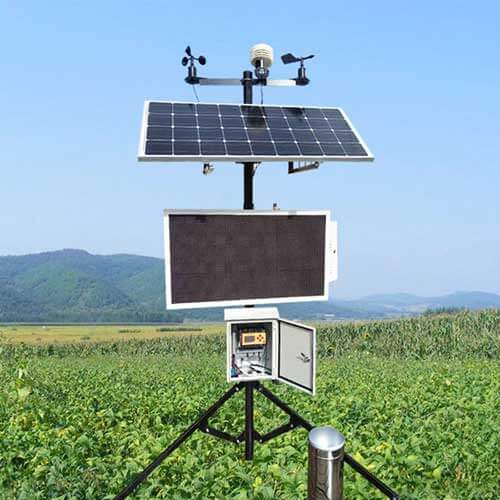
What is meteorological station?
Meteorological station is a professional equipment to collect, analyze and process weather data. By collecting and analyzing temperature, humidity, air pressure, light, rainfall, dew point, wind speed, wind direction and other meteorological elements, it predicts climate change and responds to various meteorological disasters.
The overall appearance of a meteorological station consists of a stand-alone pole supporting various weather sensors and the collection mainframe at the top. Usually the perimeter and top of the installation site are away from buildings and other obstructions to ensure the accuracy of the measurement data.
Meteorological station components
Meteorological monitoring systems generally consist of measurement unit, power supply system and control unit.
Measurement unit
Meteorological monitoring station derive their data from individual weather sensors. A completed meteorological station monitoring system includes the following sensors:
- Temperature humidity sensor
- Wind speed sensor/wind direction sensor
- Solar radiation sensor
- Rain gauge
- Rain and snow sensor
- UV sensor
- Dew point sensor
- Solar radiation shield
- Gas sensor
- Soil sensor
1. Temperature and humidity sensor
In order to prevent the impact of direct sunlight and rain erosion on the measurement data, the sensor is placed in a solar radiation shielding cover to monitor the temperature and relative humidity in the environment. Temperature and humidity are the most basic elements in meteorological research. There are many types of temperature and humidity sensors, such as resistive, capacitive, thermal, etc.
Monitoring wind speed and direction is a standard part of every weather monitoring system. Whether it is agriculture, navigation or transportation fields need to measure wind speed and direction. Wind speed and wind direction sensors work to strictly ensure that there is no obstruction around, so as to ensure that the data is true and effective. There are various types of wind speed and direction sensors such as mechanical, ultrasonic, magneto-electric and so on.

Equipment used to measure the intensity or energy of solar radiation. Solar radiation sensor can be divided into total radiation sensor, direct radiation sensor, scattered radiation sensor. According to different wavelength ranges, it can also be divided into visible radiation sensors, ultraviolet radiation sensors, infrared radiation sensors and so on. Solar radiation sensors are generally installed on horizontal or inclined platforms to facilitate the reception of sunlight, while avoiding shading and reflection from surrounding objects.
Equipment used to measure precipitation. Rain gauge can be divided into two categories of mechanical and electronic, mechanical rain gauge is mainly funnel type, bucket type, float type. Electronic rain gauge is mainly photoelectric, acoustic wave, radar and so on. Mechanical rain gauge structure is simple, inexpensive, but need to manually clean up and read data regularly. Electronic rain gauge structure is complex, high price, but can realize automation and remote observation and transmission.

It is to measure the phenomenon of rainfall and snowfall equipment. Divided into two kinds with automatic heating function and no heating function. Both need to be installed at an angle to avoid water stagnation on the surface leading to icing.
Equipment used to measure the intensity or index of ultraviolet light. UV sensors can be divided into two categories: broadband and narrowband. Broadband UV sensors can measure the intensity of radiation across the entire UV band, and narrowband UV sensors can measure the intensity of radiation in a specific wavelength range. UV sensors are generally mounted on horizontal or inclined platforms to facilitate the reception of sunlight, while avoiding shading and reflection from surrounding objects.
It is a device that can directly measure the dew point temperature. Its data also reflects the humidity of the climate. Typical dew-point sensors are thin-film capacitive, resistive, and chilled-mirror.
8. Other sensors
Common other sensors, such as atmospheric pressure sensor, illuminance sensor, noise sensor, etc. are placed in the solar radiation shield. Solar radiation shield is a device used to protect the weather sensor, it consists of a number of shutters, can effectively block the sun, rain and other external factors on the sensor interference, while maintaining good ventilation performance, so that the sensor inside and outside the air temperature is similar. In addition, other gas sensors, soil sensors, etc. are added as needed.
Power supply system
The meteorological station can support both power supply and solar power supply. Power supply usually only requires connecting the power cord to the host. The solar power supply system consists of solar panels, lead-acid batteries, waterproof boxes and controllers.
Control unit
The monitoring mainframe collects data by connecting to each weather sensor, uploads the data and supplies power to the sensors. At the same time, it can give commands to the monitoring platform. The process of data transmission relies on the cooperation of the monitoring host and various signal/power cables.
What are the types of meteorological stations?
- Agricultural weather station
- Transportation weather station
- Forest weather station
- Port weather station
- Campus weather station
Agricultural weather station
Agricultural weather stations are devices used to access climate changes in areas such as fields. Installing weather stations in wheat fields can monitor elements such as ambient temperature and humidity, wind speed and direction, and light, helping farmers to understand meteorological changes in real time and formulate agricultural measures in line with crop growth. And according to the growth stage of different crops, irrigation, fertilization and other measures. Maximum protection of crop growth and crop quality.
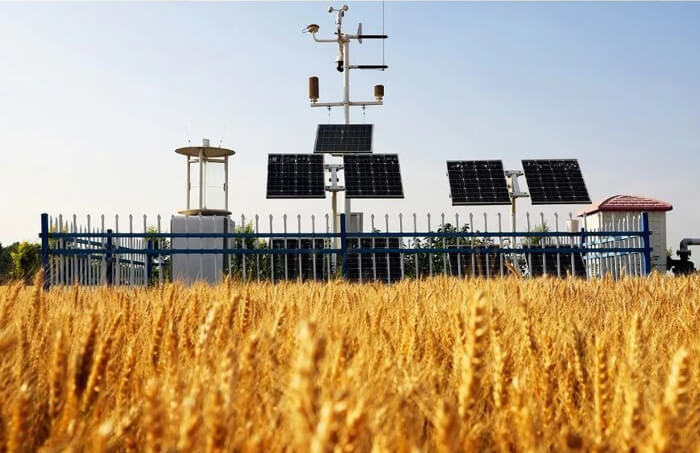

Transportation weather station
The transportation weather station is mainly used for meteorological monitoring of highways, railroads, airports and other locations. It can work automatically without manual guarding. Traffic weather station is a monitoring station designed for monitoring road weather. It focuses on monitoring visibility, meteorology and road surface water monitoring to discover abnormal environmental and meteorological conditions of each road section in time and provide decision-making basis for meteorological and traffic management departments.
A forest weather station is a specialized facility for monitoring and recording forest weather data. It combines the needs of meteorological observation and forestry management. By monitoring meteorological factors such as wind speed and direction, air temperature, relative humidity and solar radiation in areas prone to fires, it prevents forest fires from occurring and also guides relief efforts to safeguard the forest ecology after forest fires have occurred.
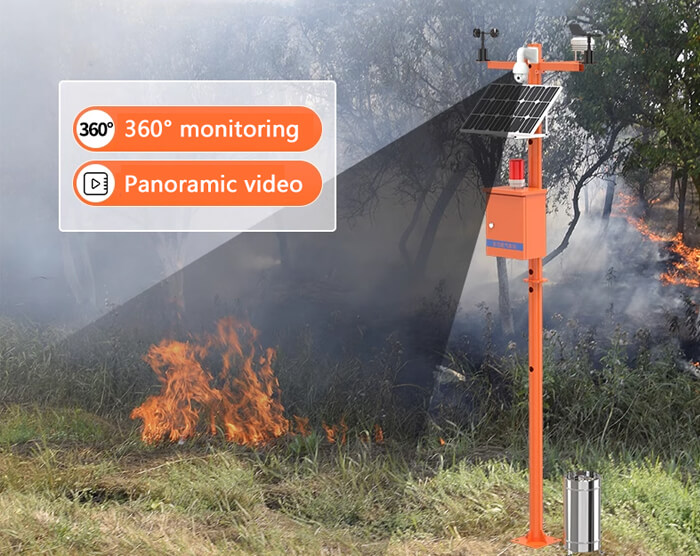

Port weather station
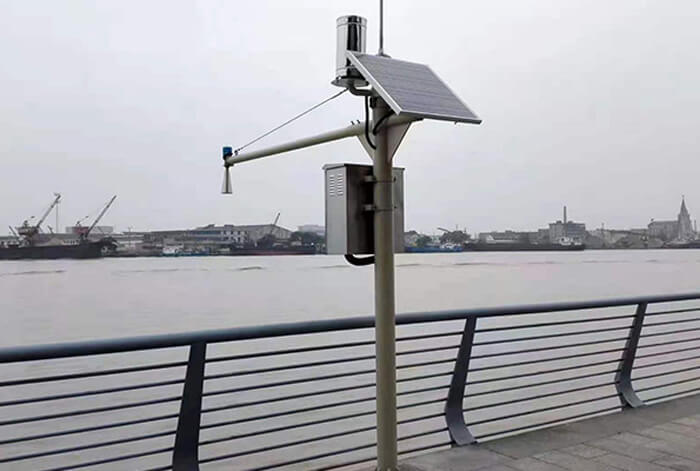
Port weather stations are mainly used for meteorological monitoring in ports. During port operations, meteorological conditions (e.g., wind speed, wind direction) affect ships and port operations. Port meteorological monitoring is crucial to port operations. Port meteorological conditions directly affect the entry and exit, loading and unloading, and berthing of ships. Meteorological monitoring by port weather stations can provide real-time meteorological data such as wind, waves, fog, visibility, etc. to help ships enter and leave the port safely under adverse weather conditions.

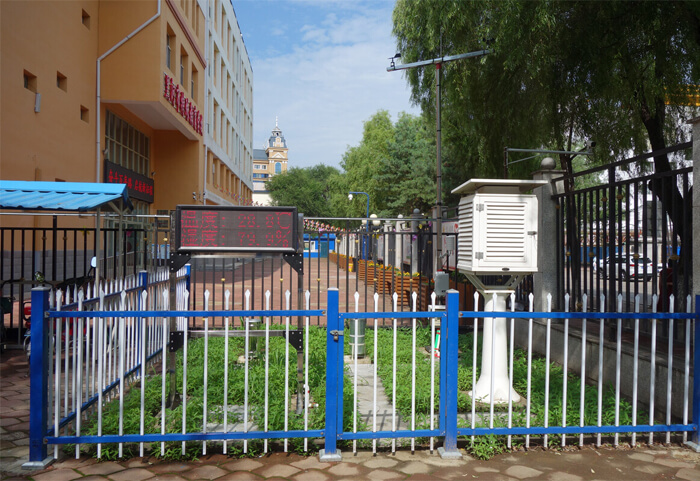
Campus weather station
Campus weather stations can help students recognize and understand various weather disasters and improve their ability to cope with weather disasters. The construction of campus weather stations can enable students to master and understand meteorological knowledge, and independently and autonomously complete meteorological observation work.

Why is meteorological station important?
1. Predict the weather
The meteorological station can be used to record a variety of weather data from the ground, atmosphere and oceans, including temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, wind direction and wind speed. Rainfall, snowfall, sunshine and ground temperature can also be measured. With these data, meteorological stations can predict future weather conditions. For example, meteorological stations can predict storms, typhoons, tornadoes and other natural disasters. This can help the government and the public to take the necessary measures so as to minimize casualties and property damage caused by weather.
2. Agricultural production
The meteorological station also have a significant impact on agricultural production. In the context of global warming and climate change, farmers need accurate weather forecasts to select appropriate crop varieties and planting times. Meteorological stations can collect and transmit data so that farmers can plan and manage crop yields based on weather forecasts.
3. Water resources management
Water resources management is very important for most countries. One of the roles of meteorological stations is to measure changes in water levels and flows in water resources. These data allow governments to formulate various water management policies to ensure that water quality and quantity are adequately protected. In addition, meteorological stations measure snow depth and the thickness of river ice so that hydropower plants can be accurately planned and managed for energy during the winter.
4. Aviation and navigation
The meteorological station can provide very important information for aviation and shipping. Pilots and ship captains can use the weather information provided by meteorological stations to determine the best time to take off and land. In addition, meteorological stations can monitor changes in wind direction and speed, thereby reducing risks to aircraft and ships.
5. Climate research
The meteorological station collect a variety of data that can provide data support for weather forecasting. It can record changes in the atmosphere and oceans so that scientists can understand the trends and causes of climate change. This data plays an important role in climate modeling and research to predict the accuracy of weather.